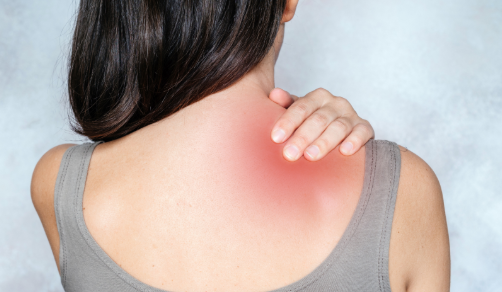
Unlocking the Mystery of Stage 1 Fibromyalgia: Recognizing the First Signs Before It Escalates
Stage 1 Fibromyalgia: Understanding the Onset of a Complex Condition
Fibromyalgia is a chronic syndrome that affects millions globally, often manifesting through widespread pain, fatigue, and cognitive disturbances. What makes it particularly challenging is that the condition does not suddenly appear in full force. It often starts subtly, progressing through stages, with Stage 1 fibromyalgia being the least understood and most overlooked. Recognizing Stage 1 can be the key to early diagnosis, better symptom management, and potentially slowing the condition’s progression.
What Is Stage 1 Fibromyalgia?
Stage 1 fibromyalgia refers to the very beginning of the fibromyalgia spectrum. This phase is marked by subtle and sporadic symptoms that may not yet form a recognizable pattern. Because they are mild and non-specific, these symptoms are frequently misattributed to everyday stress, minor illnesses, or aging. At this point, patients may not seek medical advice or may receive alternative diagnoses due to the elusive nature of the symptoms.
Common Symptoms in Stage 1
Stage 1 symptoms are often light but persistent enough to raise concern over time. These include:
- Generalized Body Aches: Early discomfort might feel like muscle soreness from overexertion, but without a clear physical cause.
- Unexplained Fatigue: Individuals often report feeling tired despite getting adequate sleep. This fatigue is not resolved with rest.
- Subtle Cognitive Issues: Referred to as “fibro fog,” early signs may include forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating, or mental sluggishness.
- Disturbed Sleep Patterns: Light, non-restorative sleep may become a recurring issue, even if insomnia has not yet developed.
- Increased Sensitivity: Individuals might notice heightened sensitivity to cold, heat, or pain in ways they did not before.
These symptoms can appear gradually and might vary in intensity day to day, making them easy to ignore or dismiss in their initial stages.
Challenges in Diagnosis at Stage 1
Stage 1 fibromyalgia is particularly hard to diagnose due to the absence of definitive laboratory tests or imaging studies that can confirm the condition. Most conventional tests will return normal results during this early phase. As a result, people are often misdiagnosed with conditions such as:
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Depression or anxiety
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Vitamin D deficiency
The diagnostic process typically becomes clearer only when symptoms intensify and begin affecting daily function more severely, often in later stages.
Risk Factors That May Trigger Stage 1
Understanding what can precipitate Stage 1 symptoms is crucial for early identification. Common triggers include:
- Physical Trauma: Accidents or surgeries may initiate chronic pain symptoms.
- Infections: Viral illnesses can spark a cascade of immune and neurological responses leading to fibromyalgia-like symptoms.
- Psychological Stress: Intense emotional stress or ongoing mental strain can alter nervous system function, potentially triggering the onset of symptoms.
- Genetics: A family history of fibromyalgia or other chronic pain conditions may increase susceptibility.
Identifying these contributing factors early could allow for more targeted interventions before the condition becomes more advanced.
Management Strategies for Stage 1 Fibromyalgia
Early management focuses on lifestyle changes and symptom monitoring rather than pharmaceutical intervention. Strategies include:
- Sleep Regulation: Establishing a consistent sleep routine and practicing good sleep hygiene can help combat early fatigue.
- Stress Reduction: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help regulate stress hormones.
- Low-Impact Exercise: Gentle physical activity such as walking, yoga, or swimming may prevent deconditioning and improve blood flow.
- Dietary Adjustments: Anti-inflammatory diets rich in omega-3s, fruits, and vegetables may support overall health.
- Tracking Symptoms: Keeping a health journal to record symptoms, triggers, and responses to lifestyle changes can help identify patterns.
Starting these interventions early may reduce the severity of symptoms and delay progression into more debilitating stages.
When to See a Doctor
Although symptoms in Stage 1 are mild, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider if they persist for more than three months, disrupt daily life, or worsen without a clear cause. Early dialogue with a physician can lead to monitoring, supportive care, and preparation for more advanced stages if they occur.
The Importance of Early Recognition
The earlier fibromyalgia is identified, the greater the chance of managing it effectively without heavy reliance on medications. Stage 1 is the critical window where lifestyle adjustments can have the most profound impact. Recognizing and addressing symptoms early allows patients to take proactive control of their health before chronic pain and fatigue become overwhelming.
Conclusion
Stage 1 fibromyalgia is often hidden in plain sight, masked by the mundane nature of its symptoms. However, it is during this stage that the greatest opportunities for positive change and effective management exist. By learning to recognize the signs, paying close attention to your body, and adopting healthy lifestyle strategies, it is possible to take a stand against the progression of fibromyalgia early on. Empowerment begins with awareness, and Stage 1 offers the foundation for building resilience in the face of chronic illness.